What is LaTeX?
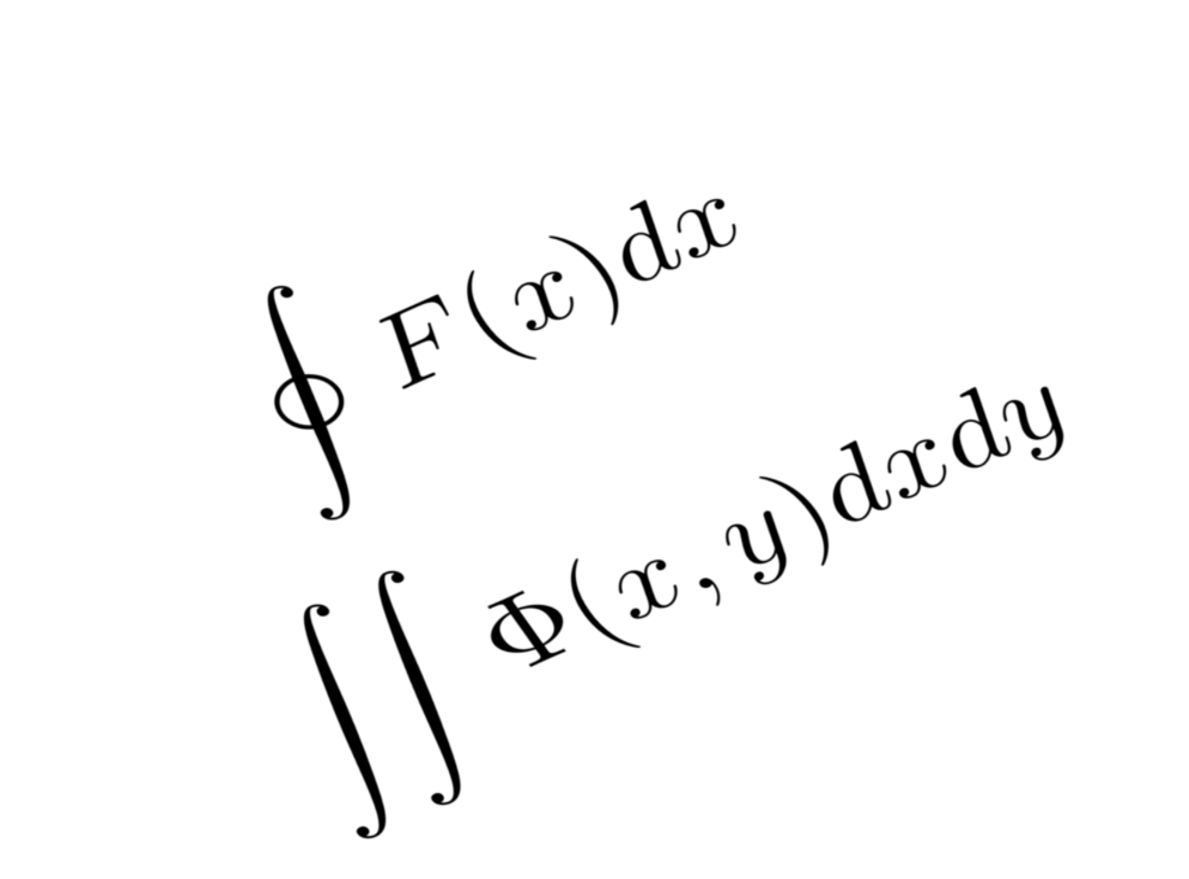
Latex is a language for high quality editing documents, especially oriented to book composition, scientific and technical documents, that include formulas and high quality images. It consists on a set of Tex macros (one low-level language) and has become almost a standard for scientific publications in areas such as mathematics, physics and engineering, since we can have finer control over any typographical appearance of the document.
Latex is not a text editor, is a language for preparing documents and therefore its appearance is not equal. The latex editors differ of the WYSIWYG editor (what you see is what you get) because latex allows users to write a paper, focusing exclusively on the content without having to worry about the format details.
Advantages of Latex
- Stable and multi-platform: the file format is more stable than the one in text editors, also there exist implementations for different platforms, and in all of them, the result is exactly the same.
- High-quality equation editing: it can set the size of the parentheses, integrals, subscript and superscript, align elements in a matrices, constructed boxes, etc.
- Ease-writing structured documents: it is possible to write texts dividing them into chapters, sections, subsections, controlling at all times numbering and cross-referencing. Automatic indexing of contents, tables or figures.
- It’s free.
Disadvantages of Latex
- Slow learning curve: it requires a learning period before getting the first results. Even medium or advanced user always have a manual nearby.
- The results are not seen until the file is compiled: no preview available until it is compiled. During this process, it is usual the appearing of compilation errors and it can be frustrating for beginners. The only solution is to be patient.
Using Latex
The document preparation normally requires two stages: the first is to create a source file using a text editor, which includes the appropriate commands and the text to be printed. The second is to compile the source file; this process consists on interpreting the written orders on the source file, leaving it ready to be sent to the corresponding output, either the screen or the pdf printer. Now, if you want to add or change something in the document, you must make the appropriate changes in the source file and compile it again.
Latex distributions
There are several latex distributions, e.g., TeXLive can be used on Linux, Mac and Windows, MacTex for OS X and MiKTeX is used in Windows. Another advantage of LaTeX is that the output is always the same, regardless of the device (printer, screen, etc..) or the operating system, and it can be exported to a variety of formats (Postscript, PDF, SGML, HTML, RTF, etc.).
Latex Editors
There are several applications that helps a person to write a document in a more visual way: Texmaker, LyX, TeXmacs, Texstudio, WinShell, Kile and others. Another easy way to edit and to produce the corresponding equations in latex code, is to use a Google Chrome browser extension called Daum Equation Editor.
Example of a Latex document
\documentclass[12pt]{article}
\usepackage[spanish]{babel}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\usepackage[latin1]{inputenc}
\title{\LaTeX}
\date{}
% This is a comment, not be displayed in the final document.
\begin{document}
\maketitle
\LaTeX es un programa para preparar documentos con el sistema de tipograf\'ias \footnote{Seg\'un Wikipedia, la tipograf\'ia es el arte y t\'ecnica del manejo y selecci\'on de tipos, originalmente de plomo, para crear trabajos de impresi\'ion} \TeX. \LaTeX fue desarrollado originalmente por Leslie Lamport en $1984$ y se convirti\'o en el m\'etodo dominante para la manipulaci\'on de \TeX. La versi\'on utilizada para generar este documento es \LaTeXe.
\newline
% The following code shows the quality of LaTeX typesetting
$$E=mc^2$$
$$\oint F(x)dx$$
$$\iint \Phi(x, y)dxdy$$
$$\begin{matrix}A\xrightarrow{\;\;\;f\;\;\;}B\\\pi\downarrow{\;\;\;\;\;}\;\;\;\uparrow{} \phi\\C\xrightarrow{\;\;\;g\;\;\;}D\end{matrix}$$
\end{document}
This code will produce a document as in Figure #1.

Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: